 Pro
Pro
Real-time news aggregation with advanced tools for professionals.
The Fastest
Way
to Watch the World
Monitor thousands of global sources in real-time. No algorithms, no clutter—just the raw feed for professionals.
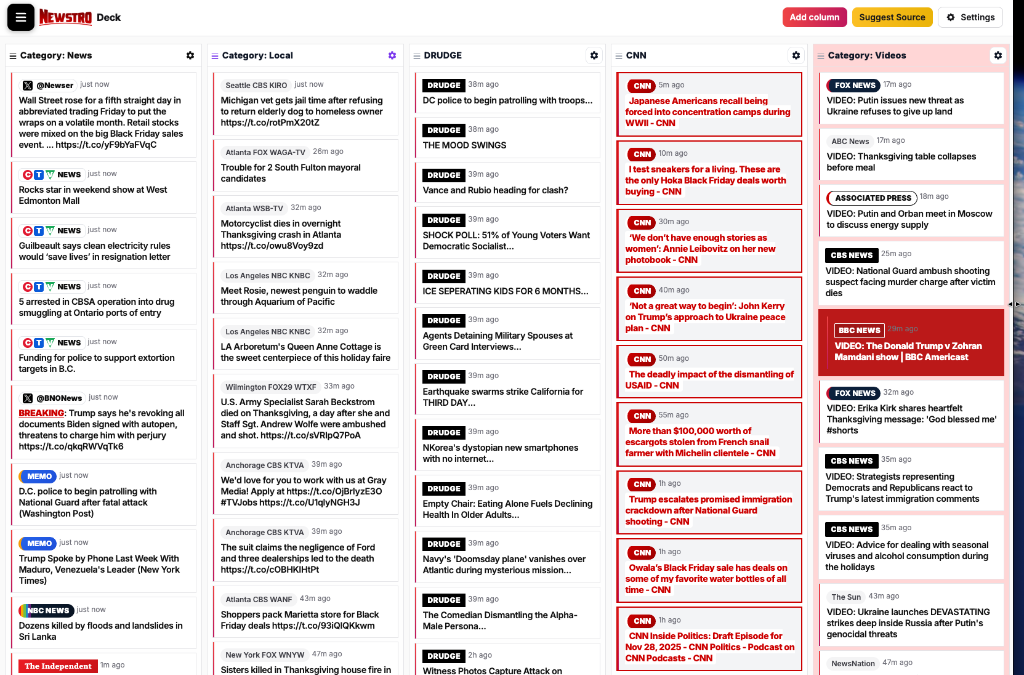
Trusted sources aggregated in real-time
Why Newstro Pro
Professional news monitoring with multi-column views, category filtering, keyword tracking, and real-time updates. Built for journalists, researchers, and news enthusiasts.
Advanced Source Control
Manage thousands of sources. Filter by category, region, or type to curate your perfect feed.
Mobile Optimized
Intelligent headline cleaning and a responsive design ensure you get the signal, not the noise, on any device.
Newstro Pro Features
- ✓ Multi-column dashboard for simultaneous monitoring
- ✓ Category filtering (Breaking, News, Politics, and more)
- ✓ Keyword trend analysis and word cloud visualization
- ✓ Real-time updates with auto-refresh
- ✓ Bookmark system to save important headlines
- ✓ Source-specific feeds and filtering
- ✓ Ad-free, distraction-free interface
- ✓ Advanced admin tools for content management
Advanced Features
Professional tools for serious news monitoring and research.
-
Keyword Trends & AnalyticsTrack trending topics with interactive graphs and word clouds
-
Category ManagementOrganize news by Breaking, Politics, Sports, and custom categories
-
Real-Time MonitoringLive updates with customizable refresh intervals and notifications
-
Bookmarks & CollectionsSave and organize important stories for later reference
What Users Say
"Newstro Pro has completely changed how I monitor news. The multi-column view and keyword tracking are essential for my work."
— Political Analyst
"The category filtering and real-time updates help me stay on top of breaking stories instantly. No more switching between tabs."
— News Researcher
"Clean interface, powerful features, zero distractions. Worth every penny."
— Pro Subscriber
Start Monitoring Now
Join professionals who rely on Newstro for real-time news monitoring
Sign Up FreeFree forever • Upgrade anytime